

Conjunctival infectionĪdult conjunctivitis can occur from auto- inoculation and is less common than neonatal conjunctivitis.

Vertical transmission from mother to child can cause neonatal conjunctivitis and, more rarely, bacterial sepsis. Gonococcal infection during pregnancy can result in miscarriage, preterm delivery and postpartum endometritis. Ascending infection in malesĪscending infection in males can cause painful inflammation and swelling of the epididymis and the testicles (epididymo-orchitis). Scarring of the female upper genital tract can lead to chronic pelvic pain, ectopic pregnancy and infertility. Ascending infection in femalesĪscending infection in females can cause pelvic inflammatory disease (endometritis, salpingitis, tubal-ovarian abscess). This is more likely to occur when the infection is asymptomatic or when there is any barrier to access health care. What is disseminated gonococcal infection?Ĭomplications of gonorrhoea occur when the infection is left undiagnosed and untreated. Pharyngeal infection is becoming increasingly common particularly in men who have sex with men (MSM) and is largely asymptomatic.
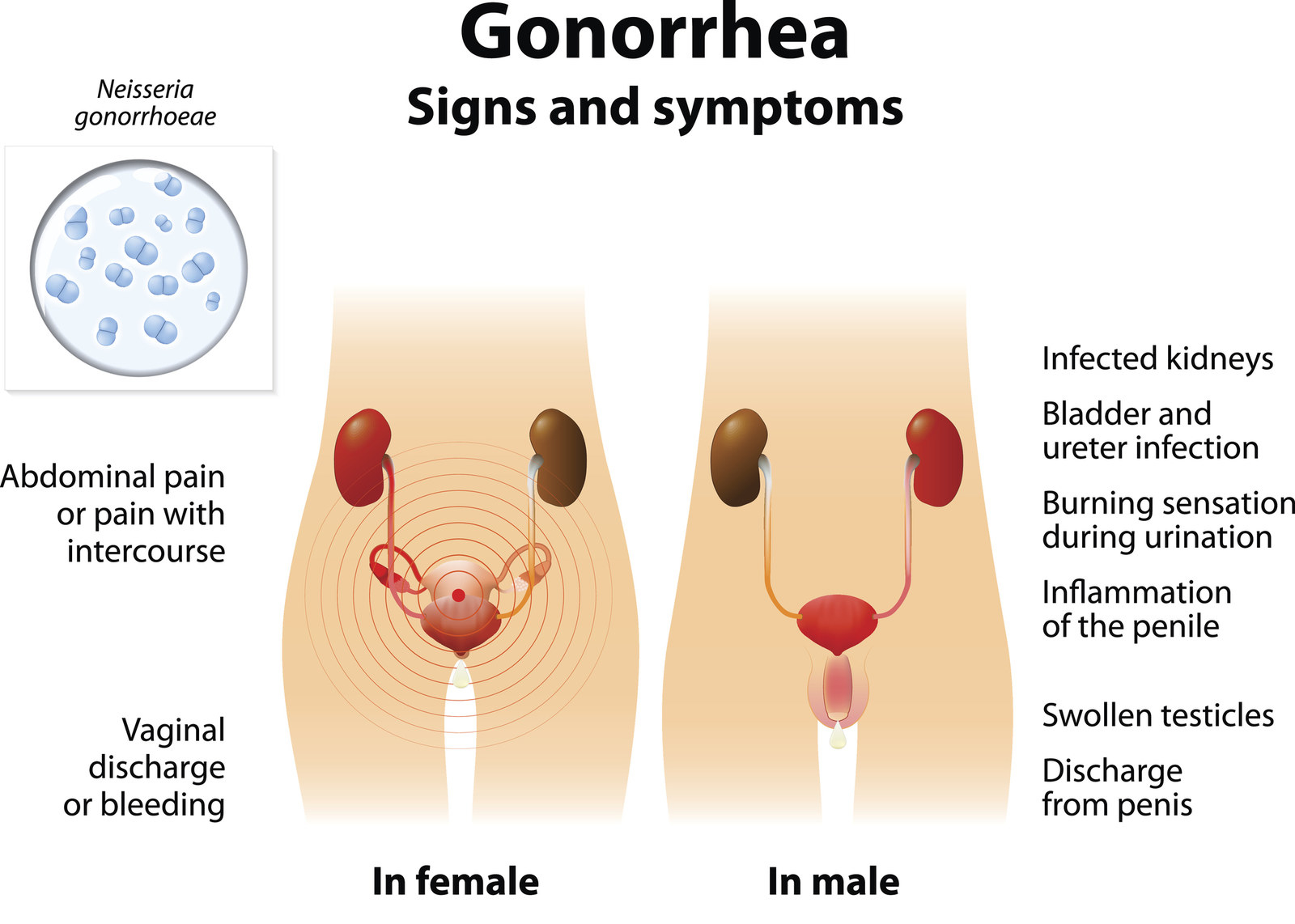
Safer sex means using a condom or oral dam during sexual activity, which may include vaginal, oral or anal contact. People at risk of gonorrhoea are mainly sexually active people that come in contact with an infected person while not practising safer sex. If the mother is infected, gonorrhoea may also be passed to a newborn delivered vaginally causing conjunctivitis. Gonorrhoea is a sexually transmitted infection (STI). The common sites of infection are the mucous membranes of the urethra, endocervix, rectum, pharynx and conjunctiva. Gonorrhoea is a disease is due to infection with the bacteria Neisseria gonorrhoeae.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
